Polynomial Approximations and Series - AP Calculus BC
Card 1 of 1140
Which of the following series does not converge?
Which of the following series does not converge?
Tap to reveal answer
We can show that the series  diverges using the ratio test.
diverges using the ratio test.
![L = \lim_{n ->\infty } \frac{a_{n+1}}{a_{n}} = \lim_{n ->\infty } \left[\left(\frac{(n+1)!}{(n+1)^2 cos (n+1)} \div \frac{n!}{n^2 cos (n) }\right)\right]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/343419/gif.latex)

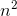 will dominate over
will dominate over  since it's a higher order term. Clearly, L will not be less than, which is necessary for absolute convergence.
since it's a higher order term. Clearly, L will not be less than, which is necessary for absolute convergence.
Alternatively, it's clear that  is much greater than
is much greater than  , and thus having
, and thus having  in the numerator will make the series diverge by the
in the numerator will make the series diverge by the  limit test (since the terms clearly don't converge to zero).
limit test (since the terms clearly don't converge to zero).
The other series will converge by alternating series test, ratio test, geometric series, and comparison tests.
We can show that the series 
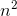

Alternatively, it's clear that 



The other series will converge by alternating series test, ratio test, geometric series, and comparison tests.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Determine whether

converges or diverges, and explain why.
Determine whether
converges or diverges, and explain why.
Tap to reveal answer
We can use the alternating series test to show that

converges.
We must have  for
for  in order to use this test. This is easy to see because
in order to use this test. This is easy to see because  is in
is in![\small \small \left[0,\frac{\pi}{2}\right]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/385614/gif.latex) for all
for all  (the values of this sequence are
(the values of this sequence are  ), and sine is always nonzero whenever sine's argument is in
), and sine is always nonzero whenever sine's argument is in ![\small \small \left[0,\frac{\pi}{2}\right]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/385615/gif.latex) .
.
Now we must show that
1. 
2.  is a decreasing sequence.
is a decreasing sequence.
The limit

implies that

so the first condition is satisfied.
We can show that  is decreasing by taking its derivative and showing that it is less than
is decreasing by taking its derivative and showing that it is less than  for
for  :
:

The derivative is less than  , because
, because  is always less than
is always less than  , and that
, and that  is positive for
is positive for  , using a similar argument we used to prove that
, using a similar argument we used to prove that  for
for  . Since the derivative is less than
. Since the derivative is less than  ,
,  is a decreasing sequence. Now we have shown that the two conditions are satisfied, so we have proven that
is a decreasing sequence. Now we have shown that the two conditions are satisfied, so we have proven that

converges, by the alternating series test.
We can use the alternating series test to show that
converges.
We must have 


![\small \small \left[0,\frac{\pi}{2}\right]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/385614/gif.latex)


![\small \small \left[0,\frac{\pi}{2}\right]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/385615/gif.latex)
Now we must show that
1.
2. 
The limit
implies that
so the first condition is satisfied.
We can show that 


The derivative is less than 








converges, by the alternating series test.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Determine whether the following series converges or diverges:

Determine whether the following series converges or diverges:
Tap to reveal answer
Given just the harmonic series, we would state that the series diverges. However, we are given the alternating harmonic series. To determine whether this series will converge or diverge, we must use the Alternating Series test.
The test states that for a given series  where
where  or
or  where
where  for all n, if
for all n, if  and
and  is a decreasing sequence, then
is a decreasing sequence, then  is convergent.
is convergent.
First, we must evaluate the limit of  as n approaches infinity:
as n approaches infinity:

The limit equals zero because the numerator of the fraction equals zero as n approaches infinity.
Next, we must determine if  is a decreasing sequence.
is a decreasing sequence.  , thus the sequence is decreasing.
, thus the sequence is decreasing.
Because both parts of the test passed, the series is (absolutely) convergent.
Given just the harmonic series, we would state that the series diverges. However, we are given the alternating harmonic series. To determine whether this series will converge or diverge, we must use the Alternating Series test.
The test states that for a given series 






First, we must evaluate the limit of 
The limit equals zero because the numerator of the fraction equals zero as n approaches infinity.
Next, we must determine if 

Because both parts of the test passed, the series is (absolutely) convergent.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Consider:  . Will the series converge or diverge? If converges, where does this coverge to?
. Will the series converge or diverge? If converges, where does this coverge to?
Consider: 
Tap to reveal answer
This is a geometric series. Use the following formula, where  is the first term of the series, and
is the first term of the series, and  is the ratio that must be less than 1. If
is the ratio that must be less than 1. If  is greater than 1, the series diverges.
is greater than 1, the series diverges.

Rationalize the denominator.

This is a geometric series. Use the following formula, where 


Rationalize the denominator.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Consider the following summation:  . Does this converge or diverge? If it converges, where does it approach?
. Does this converge or diverge? If it converges, where does it approach?
Consider the following summation: 
Tap to reveal answer
The problem can be reconverted using a summation symbol, and it can be seen that this is geometric.

Since the ratio is less than 1, this series will converge. The formula for geometric series is:

where  is the first term, and
is the first term, and  is the common ratio. Substitute these values and solve.
is the common ratio. Substitute these values and solve.

The problem can be reconverted using a summation symbol, and it can be seen that this is geometric.
Since the ratio is less than 1, this series will converge. The formula for geometric series is:
where 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A worm crawls up a wall during the day and slides down slowly during the night. The first day the worm crawls one meter up the wall. The first night the worm slides down a third of a meter. The second day the worm regains one third of the lost progress and slides down one third of that distance regained on the second night. This pattern of motion continues...
Which of the following is a geometric sum representing the distance the worm has travelled after  12-hour periods of motion? (Assuming day and night are both 12 hour periods).
12-hour periods of motion? (Assuming day and night are both 12 hour periods).
A worm crawls up a wall during the day and slides down slowly during the night. The first day the worm crawls one meter up the wall. The first night the worm slides down a third of a meter. The second day the worm regains one third of the lost progress and slides down one third of that distance regained on the second night. This pattern of motion continues...
Which of the following is a geometric sum representing the distance the worm has travelled after 
Tap to reveal answer
The sum must be alternating, and after one period you should have the worm at 1m. After two periods, the worm should be at 2/3m. There is only one sum for which that is true.
The sum must be alternating, and after one period you should have the worm at 1m. After two periods, the worm should be at 2/3m. There is only one sum for which that is true.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Determine what the following series converges to, and whether the series is Convergent, Divergent or Neither.

Determine what the following series converges to, and whether the series is Convergent, Divergent or Neither.
Tap to reveal answer
To determine if

is convergent, divergent or neither, we need to use the ratio test.
The ratio test is as follows.
Suppose we a series  . Then we define,
. Then we define,
 .
.
If
 the series is absolutely convergent (and hence convergent).
the series is absolutely convergent (and hence convergent).
 the series is divergent.
the series is divergent.
 the series may be divergent, conditionally convergent, or absolutely convergent.
the series may be divergent, conditionally convergent, or absolutely convergent.
Now lets apply this to our situtation.
Let

and

Now

We can rearrange the expression to be

We can simplify the expression to

When we evaluate the limit, we get.
 .
.
Since  , we have sufficient evidence to conclude that the series is Convergent.
, we have sufficient evidence to conclude that the series is Convergent.
To determine if
is convergent, divergent or neither, we need to use the ratio test.
The ratio test is as follows.
Suppose we a series 

If



Now lets apply this to our situtation.
Let
and
Now
We can rearrange the expression to be
We can simplify the expression to
When we evaluate the limit, we get.

Since 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Determine whether the following series converges or diverges. If it converges, what does it converge to?

Determine whether the following series converges or diverges. If it converges, what does it converge to?
Tap to reveal answer
First, we reduce the series into a simpler form.

We know this series converges because

By the Geometric Series Theorem, the sum of this series is given by

First, we reduce the series into a simpler form.
We know this series converges because
By the Geometric Series Theorem, the sum of this series is given by
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Calculate the sum of a geometric series with the following values: ,
, ,
, . Round the answer to the nearest integer.
. Round the answer to the nearest integer.
Calculate the sum of a geometric series with the following values:


Tap to reveal answer
This is a geometric series.
The sum of a geometric series can be calculated with the following formula,
 , where n is the number of terms to sum up, r is the common ratio, and
, where n is the number of terms to sum up, r is the common ratio, and  is the value of the first term.
is the value of the first term.
For this question, we are given all of the information we need.
Solution:





Rounding, 
This is a geometric series.
The sum of a geometric series can be calculated with the following formula,


For this question, we are given all of the information we need.
Solution:
Rounding,
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Calculate the sum of a geometric series with the following values:
 ,
, ,
, ,
,
rounded to the nearest integer.
Calculate the sum of a geometric series with the following values:



rounded to the nearest integer.
Tap to reveal answer
This is a geometric series.
The sum of a geometric series can be calculated with the following formula,
 , where n is the number of terms to sum up, r is the common ratio, and
, where n is the number of terms to sum up, r is the common ratio, and  is the value of the first term.
is the value of the first term.
For this question, we are given all of the information we need.
Solution:





Rounding, 
This is a geometric series.
The sum of a geometric series can be calculated with the following formula,


For this question, we are given all of the information we need.
Solution:
Rounding,
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Calculate the sum, rounded to the nearest integer, of the first 16 terms of the following geometric series: 
Calculate the sum, rounded to the nearest integer, of the first 16 terms of the following geometric series:
Tap to reveal answer
This is a geometric series.
The sum of a geometric series can be calculated with the following formula,
 , where n is the number of terms to sum up, r is the common ratio, and
, where n is the number of terms to sum up, r is the common ratio, and  is the value of the first term.
is the value of the first term.
We have  and n and we just need to find r before calculating the sum.
and n and we just need to find r before calculating the sum.
Solution:






This is a geometric series.
The sum of a geometric series can be calculated with the following formula,


We have 
Solution:
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Use the ratio test to determine if the series diverges or converges:

Use the ratio test to determine if the series diverges or converges:
Tap to reveal answer



This limit is infinite, so the series diverges.
This limit is infinite, so the series diverges.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
One of the following infinite series CONVERGES. Which is it?
One of the following infinite series CONVERGES. Which is it?
Tap to reveal answer
 converges due to the comparison test.
converges due to the comparison test.
We start with the equation  . Since
. Since  for all values of k, we can multiply both side of the equation by the inequality and get
for all values of k, we can multiply both side of the equation by the inequality and get  for all values of k. Since
for all values of k. Since  is a convergent p-series with
is a convergent p-series with  ,
,  hence also converges by the comparison test.
hence also converges by the comparison test.

We start with the equation 





← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Determine the nature of convergence of the series having the general term:

Determine the nature of convergence of the series having the general term:
Tap to reveal answer
We will use the Limit Comparison Test to establish this result.
We need to note that the following limit

goes to 1 as n goes to infinity.
Therefore the series have the same nature. They either converge or diverge at the same time.
We will focus on the series:
 .
.
We know that this series is convergent because it is a p-series. (Remember that
 converges if p>1 and we have p=3/2 which is greater that one in this case)
converges if p>1 and we have p=3/2 which is greater that one in this case)
By the Limit Comparison Test, we deduce that the series is convergent, and that is what we needed to show.
We will use the Limit Comparison Test to establish this result.
We need to note that the following limit
goes to 1 as n goes to infinity.
Therefore the series have the same nature. They either converge or diverge at the same time.
We will focus on the series:

We know that this series is convergent because it is a p-series. (Remember that

By the Limit Comparison Test, we deduce that the series is convergent, and that is what we needed to show.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Does the series  converge conditionally, absolutely, or diverge?
converge conditionally, absolutely, or diverge?
Does the series 
Tap to reveal answer
The series converges conditionally.
The absolute values of the series  is a divergent p-series with
is a divergent p-series with  .
.
However, the the limit of the sequence  and it is a decreasing sequence.
and it is a decreasing sequence.
Therefore, by the alternating series test, the series converges conditionally.
The series converges conditionally.
The absolute values of the series 

However, the the limit of the sequence 
Therefore, by the alternating series test, the series converges conditionally.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following tests will help determine whether  is convergent or divergent, and why?
is convergent or divergent, and why?
Which of the following tests will help determine whether 
Tap to reveal answer
The series  is a harmonic series.
is a harmonic series.
The Nth term test and the Divergent test may not be used to determine whether this series converges, since this is a special case. The root test also does not apply in this scenario.
According the the P-series Test,  must converge only if
must converge only if  . Therefore this could be a valid test, but a wrong definition as the answer choice since the series diverge for
. Therefore this could be a valid test, but a wrong definition as the answer choice since the series diverge for  .
.
This leaves us with the Integral Test.

Since the improper integral diverges, so does the series.
The series 
The Nth term test and the Divergent test may not be used to determine whether this series converges, since this is a special case. The root test also does not apply in this scenario.
According the the P-series Test, 


This leaves us with the Integral Test.
Since the improper integral diverges, so does the series.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Use the ratio test to determine if this series diverges or converges:

Use the ratio test to determine if this series diverges or converges:
Tap to reveal answer



Since the limit is less than 1, the series converges.
Since the limit is less than 1, the series converges.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of these series cannot be tested for convergence/divergence properly using the ratio test? (Which of these series fails the ratio test?)
Which of these series cannot be tested for convergence/divergence properly using the ratio test? (Which of these series fails the ratio test?)
Tap to reveal answer
The ratio test fails when  . Otherwise the series converges absolutely if
. Otherwise the series converges absolutely if  , and diverges if
, and diverges if  .
.
Testing the series  , we have
, we have

Hence the ratio test fails here. (It is likely obvious to the reader that this series diverges already. However, we must remember that all intuition in mathematics requires rigorous justification. We are attempting that here.)
The ratio test fails when 


Testing the series 
Hence the ratio test fails here. (It is likely obvious to the reader that this series diverges already. However, we must remember that all intuition in mathematics requires rigorous justification. We are attempting that here.)
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
We consider the following series:

Determine the nature of the convergence of the series.
We consider the following series:
Determine the nature of the convergence of the series.
Tap to reveal answer
We will use the comparison test to prove this result. We must note the following:
 is positive.
is positive.
We have all natural numbers n:
 , this implies that
, this implies that
 .
.
Inverting we get :

Summing from 1 to  , we have
, we have

We know that the  is divergent. Therefore by the comparison test:
is divergent. Therefore by the comparison test:

is divergent
We will use the comparison test to prove this result. We must note the following:

We have all natural numbers n:


Inverting we get :
Summing from 1 to 
We know that the 
is divergent
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
We know that :
 and
and 
We consider the series having the general term:

Determine the nature of the series:

We know that :

We consider the series having the general term:
Determine the nature of the series:
Tap to reveal answer
We know that:
 and therefore we deduce :
and therefore we deduce :

We will use the Comparison Test with this problem. To do this we will look at the function in general form  .
.
We can do this since,
 and
and  approach zero as n approaches infinity. The limit of our function becomes,
approach zero as n approaches infinity. The limit of our function becomes,

This last part gives us  .
.
Now we know that  and noting that
and noting that  is a geometric series that is convergent.
is a geometric series that is convergent.
We deduce by the Comparison Test that the series
having general term  is convergent.
is convergent.
We know that:

We will use the Comparison Test with this problem. To do this we will look at the function in general form 
We can do this since,


This last part gives us 
Now we know that 

We deduce by the Comparison Test that the series
having general term 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →